Indiana’s diverse climate and geography present unique challenges and opportunities for gardeners and plant enthusiasts. In this article, we’ll explore Indiana’s plant hardiness zone, providing insights into its climate, suitable plant selections, and practical gardening tips tailored to the region’s specific conditions.
I. Introduction
A. Importance of Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
Plant hardiness zones play a crucial role in guiding gardeners in selecting plants that are best suited to their local climate and environmental conditions. By understanding the plant hardiness zone of their region, gardeners can make informed decisions about which plants to grow and how to care for them effectively.
B. Overview of Plant Hardiness Zones
Plant hardiness zones are determined based on average annual minimum temperatures and serve as a guideline for determining which plants are likely to thrive in a particular area. Each zone is assigned a numerical designation, with lower numbers representing colder climates and higher numbers indicating warmer regions.
C. Purpose of the Article
The purpose of this article is to provide gardeners in Indiana with valuable information about their plant hardiness zone, including climate considerations, suitable plant selections, and practical gardening tips. By understanding Indiana’s plant hardiness zone, gardeners can optimize their gardening efforts and maximize the success of their plants.
II. Indiana’s Plant Hardiness Zone
A. Climate and Environmental Factors
Indiana’s climate is characterized by four distinct seasons, with hot summers, cold winters, and moderate temperatures in spring and fall. The state’s diverse geography, including flat plains, rolling hills, and river valleys, contributes to variations in temperature, precipitation, and soil conditions across different regions.
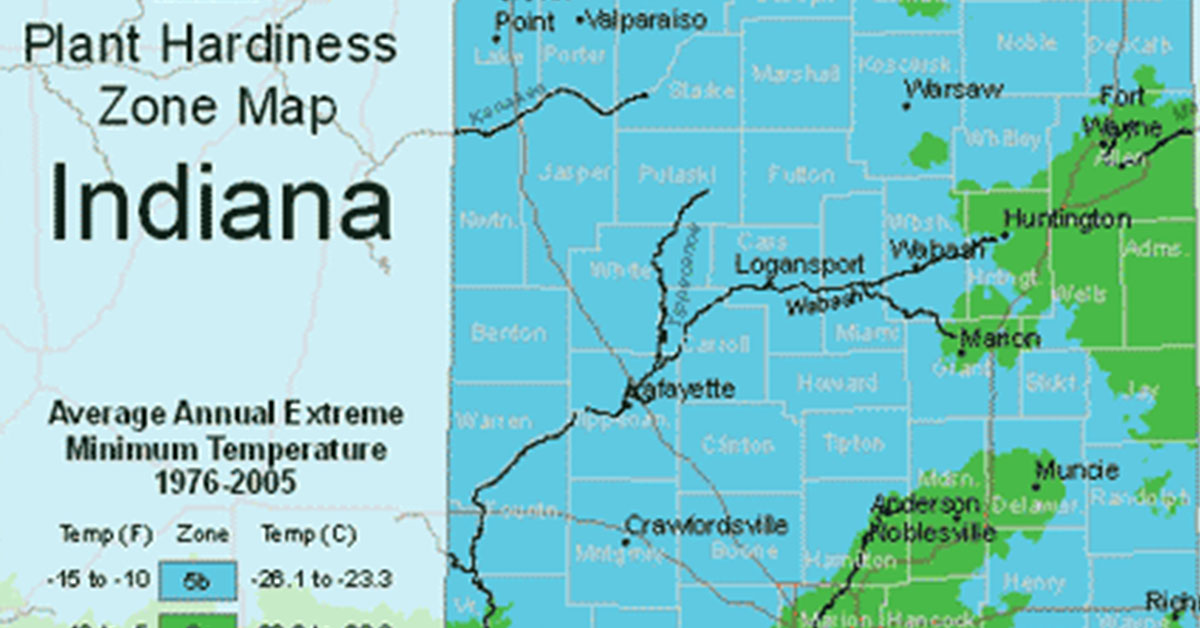
B. USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
According to the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, Indiana is primarily located in zones 5b and 6a, with some areas in the northern part of the state classified as zone 5a. These zones are defined by average annual minimum temperatures ranging from -15°F to 0°F in zone 5a, -10°F to -5°F in zone 5b, and -5°F to 0°F in zone 6a.
C. Specific Challenges and Considerations
While Indiana’s plant hardiness zones offer a wide range of gardening opportunities, gardeners may face specific challenges such as temperature fluctuations, heavy clay soils, and occasional extreme weather events. Understanding these challenges and adapting gardening practices accordingly can help gardeners overcome obstacles and achieve success in their gardens.
III. Plants Suitable for Indiana’s Zone
A. Native Plants
Native plants are well-adapted to Indiana’s climate and soil conditions, making them excellent choices for gardens and landscapes. Examples of native plants suitable for Indiana’s zone include wildflowers such as coneflowers and black-eyed Susans, grasses like switchgrass and little bluestem, and trees such as oak and maple.
B. Perennials and Annuals
Perennials and annuals that are hardy to Indiana’s zone offer a wide range of colors, textures, and bloom times for gardeners to enjoy throughout the growing season. Popular choices include daylilies, hostas, sedums, and salvias for perennials, and petunias, marigolds, zinnias, and cosmos for annuals.
C. Trees, Shrubs, and Vines
Trees, shrubs, and vines are essential elements of Indiana’s landscapes, providing shade, privacy, and visual interest. Suitable choices for Indiana’s zone include flowering trees such as dogwood and redbud, shrubs like hydrangea and viburnum, and vines such as clematis and honeysuckle.
IV. Gardening Tips for Indiana’s Zone
A. Soil Preparation and Amendment
Preparing the soil properly is essential for successful gardening in Indiana’s zone. Amend heavy clay soils with organic matter such as compost or aged manure to improve drainage and soil structure. Conduct soil tests to determine pH levels and nutrient deficiencies, and adjust soil amendments accordingly.
B. Planting and Maintenance Practices
When planting in Indiana’s zone, choose appropriate planting times and spacing recommendations for each plant species. Provide adequate water, especially during dry periods, and mulch around plants to conserve soil moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Prune trees, shrubs, and perennials as needed to promote healthy growth and flowering.
C. Seasonal Considerations and Challenges
Be mindful of seasonal considerations and challenges when gardening in Indiana’s zone. Protect tender plants from late spring frosts and early fall freezes by covering them with frost blankets or cloths. Monitor plants for signs of heat stress during hot summer months and provide shade or additional watering as needed to prevent wilting and damage.
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Indiana’s Plant Hardiness Zone
In conclusion, Indiana’s plant hardiness zone encompasses zones 5b and 6a, with variations in temperature and climate across different regions of the state. Understanding Indiana’s plant hardiness zone is essential for selecting suitable plants and implementing effective gardening practices.
B. Importance of Adapting Gardening Practices
By adapting gardening practices to suit Indiana’s zone, gardeners can overcome challenges and create thriving gardens and landscapes. Whether planting native species, selecting hardy perennials and annuals, or implementing soil preparation and maintenance techniques, understanding Indiana’s zone is key to gardening success.
C. Encouragement for Gardeners to Explore and Experiment
Finally, I encourage gardeners in Indiana to explore and experiment with a diverse range of plants and gardening techniques suited to their zone. By embracing the unique opportunities and challenges of gardening in Indiana’s zone, gardeners can create beautiful and resilient landscapes that bring joy and beauty to their homes and communities.


