I. Introduction to the 6 Petal White Flower with Yellow Center
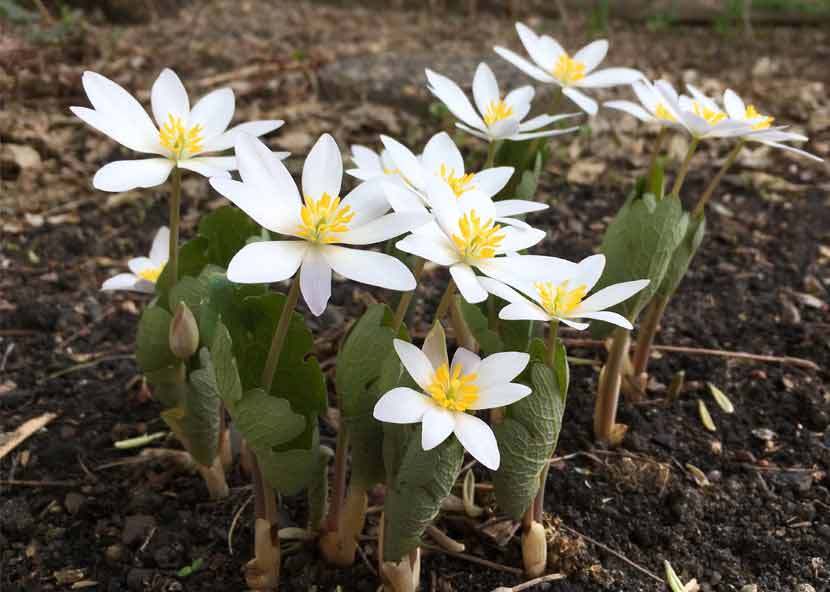
A. Overview of the Flower: The 6 petal white flower with a yellow center is a captivating floral specimen admired for its elegant beauty and distinctive color contrast.
B. Botanical Classification: Belonging to the plant kingdom, this flower falls under a specific botanical classification, exhibiting unique characteristics that distinguish it from other floral species.
C. Common Names and Varieties: Known by various common names across different regions, this flower encompasses a range of varieties, each with its own subtle variations in appearance and growth habits.
II. Characteristics of the 6 Petal White Flower
A. Physical Description 1. Petal Structure and Arrangement: The flower typically features six delicate petals arranged symmetrically around a prominent yellow center, creating a visually striking display. 2. Color Variations and Markings: While predominantly white in color, some varieties may exhibit subtle variations or markings on the petals, adding to the flower’s allure and charm.
B. Floral Anatomy 1. Stamens and Pistils: The central yellow disc contains the reproductive structures of the flower, including stamens bearing pollen and pistils responsible for fertilization. 2. Ovary and Pollination Mechanisms: Pollination occurs as insects visit the flower, transferring pollen between individual blooms and facilitating the development of seeds within the ovary.
C. Growth Habit and Lifespan 1. Plant Size and Form: Depending on the species or variety, the plant may vary in size and growth habit, ranging from compact mounds to sprawling bushes or climbing vines. 2. Bloom Season and Duration: The flower typically blooms during specific seasons, with each bloom lasting for a certain period before fading and making way for new growth.
III. Habitat and Growing Conditions
A. Natural Habitat 1. Geographic Distribution: The flower is found in diverse geographic regions, ranging from temperate climates to tropical environments around the world. 2. Preferred Ecosystems and Soil Types: It thrives in various ecosystems, including meadows, woodlands, and gardens, preferring well-drained soil with adequate moisture.
B. Cultivation Requirements 1. Sunlight and Temperature Preferences: The flower prefers full sun to partial shade, requiring adequate sunlight for healthy growth and vibrant blooms. It also has specific temperature preferences, thriving in moderate to warm climates. 2. Moisture and Watering Needs: While tolerant of some drought conditions, the plant benefits from regular watering during dry periods to maintain optimal moisture levels in the soil.
C. Maintenance and Care 1. Pruning and Deadheading: Regular pruning helps promote healthy growth and flowering, while deadheading spent blooms encourages continuous blooming throughout the season. 2. Fertilization and Soil Amendments: Applying balanced fertilizer and organic amendments enriches the soil, providing essential nutrients for robust growth and prolific flowering.
IV. Symbolism and Cultural Significance
A. Historical Associations 1. Mythological and Folkloric References: Throughout history, the flower has been associated with various myths, legends, and cultural beliefs, symbolizing themes of purity, beauty, and renewal. 2. Traditional Uses and Practices: In many cultures, the flower holds traditional significance, often used in ceremonies, rituals, and symbolic gestures to convey messages of love, admiration, or remembrance.
B. Modern Symbolism 1. Meaning in Art and Literature: The flower continues to inspire artists, poets, and writers, serving as a muse for creative expression and symbolizing diverse themes and emotions in literature and art. 2. Significance in Floral Arrangements and Events: It is a popular choice for floral arrangements in weddings, celebrations, and special occasions, representing purity, innocence, and new beginnings.
C. Cultural Interpretations 1. Spiritual and Religious Symbolism: In various spiritual traditions and religions, the flower carries symbolic significance, often representing divine qualities, enlightenment, or spiritual awakening. 2. Social and Emotional Connotations: Beyond its religious and spiritual symbolism, the flower holds personal and emotional meanings for many individuals, evoking feelings of joy, hope, and gratitude.
V. Uses and Applications
A. Ornamental Value 1. Garden Landscaping: The flower adds visual interest and aesthetic appeal to garden landscapes, serving as focal points in flower beds, borders, and containers. 2. Floral Design and Bouquets: Florists and enthusiasts incorporate the flower into floral arrangements and bouquets, creating stunning displays for various occasions and events.
B. Medicinal and Therapeutic Uses 1. Traditional Remedies and Herbal Medicine: In some cultures, parts of the flower are used in traditional remedies and herbal medicine for their purported medicinal properties, including anti-inflammatory and soothing effects. 2. Contemporary Research and Applications: Ongoing research explores the potential health benefits of the flower, with some studies investigating its antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-anxiety properties.
C. Culinary and Edible Uses 1. Culinary Applications in Cooking: Certain varieties of the flower are edible and used in culinary preparations, adding a delicate flavor and decorative touch to dishes such as salads, desserts, and beverages. 2. Edible Flowers in Gastronomy and Beverages: Chefs and mixologists incorporate edible flowers, including the 6 petal white flower with a yellow center, into gourmet dishes, cocktails, and herbal infusions for their unique flavors and visual appeal.